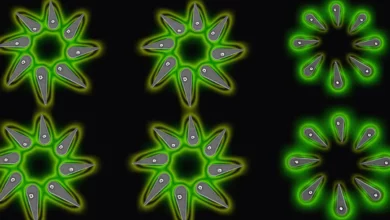
Lead Image: A ring of superconducting qubits can host “bound states” of microwave photons, where the photons tend to clump on neighboring qubit sites. Credit: Google Quantum AI
Using a quantum processor, researchers made microwave photons uncharacteristically sticky. After coaxing them to clump together into bound states, they discovered that these photon clusters survived in a regime where they were expected to dissolve into their usual, solitary states. As the finding was first made on a quantum processor, it marks the growing role that these platforms are playing in studying quantum dynamics.
Photons — quantum packets of electromagnetic radiation like light or microwaves — usually don’t interact with one another. For example, two crossed flashlight beams pass through one another undisturbed. However, microwave photons can be made to interact in an array of superconducting qubits.
Researchers at Google Quantum AI describe how they engineered this unusual situation in “Formation of robust bound states of interacting photons,” which was published on December 7 in the journal Nature. They investigated a ring of 24 superconducting qubits that could host microwave photons. By applying quantum gates to pairs of neighboring qubits, photons could travel around by hopping between neighboring sites and interacting with nearby photons.
The interactions between the photons affected their so-called “phase.” The phase keeps track of the oscillation of the photon’s wavefunction. When the photons are non-interacting, their phase accumulation is rather uninteresting. Like a well-rehearsed choir, they’re all in sync with one another. In this case, a photon that was initially next to another photon can hop away from its neighbor without getting out of sync. Just as every person in the choir contributes to the song, every possible path the photon can take contributes to the photon’s overall wavefunction. A group of photons initially clustered on neighboring sites will evolve into a superposition of all possible paths each photon might have taken.
When photons interact with their neighbors, this is no longer the case. If one photon hops away from its neighbor, its rate of phase accumulation changes, becoming out of sync with its neighbors. All paths in which the photons split apart overlap, leading to destructive interference. It would be like each choir member singing at their own pace — the song itself gets washed out, becoming impossible to discern through the din of the individual singers. Among all the possible configuration paths, the only possible scenario that survives is the configuration in which all photons remain clustered together in a bound state. This is why interaction can enhance and lead to the formation of a bound state: by suppressing all other possibilities in which photons are not bound together.
To rigorously show that the bound states indeed behaved just as particles did, with well-defined quantities such as energy and momentum, researchers developed new techniques to measure how the energy of the particles changed with momentum. By analyzing how the correlations between photons varied with time and space, they were able to reconstruct the so-called “energy-momentum dispersion relation,” confirming the particle-like nature of the bound states.
The existence of the bound states in itself was not new — in a regime called the “integrable regime,” where the dynamics is much less complicated, the bound states were already predicted and observed ten years ago. But beyond integrability, chaos reigns. Before this experiment, it was reasonably assumed that the bound states would fall apart in the midst of chaos. To test this, the researchers pushed beyond integrability by adjusting the simple ring geometry to a more complex, gear-shaped network of connected qubits. They were surprised to find that bound states persisted well into the chaotic regime.
The team at Google Quantum AI is still unsure where these bound states derive their unexpected resilience, but it could have something to do with a phenomenon called “prethermalization,” where incompatible energy scales in the system can prevent a system from reaching thermal equilibrium as quickly as it otherwise would.
Researchers anticipate that studying this system will provide fresh insights into many-body quantum dynamics and inspire more fundamental physics discoveries using quantum processors.
Reference: “Formation of robust bound states of interacting microwave photons” by A. Morvan, T. I. Andersen, X. Mi, C. Neill, A. Petukhov, K. Kechedzhi, D. A. Abanin, A. Michailidis, R. Acharya, F. Arute, K. Arya, A. Asfaw, J. Atalaya, J. C. Bardin, J. Basso, A. Bengtsson, G. Bortoli, A. Bourassa, J. Bovaird, L. Brill, M. Broughton, B. B. Buckley, D. A. Buell, T. Burger, B. Burkett, N. Bushnell, Z. Chen, B. Chiaro, R. Collins, P. Conner, W. Courtney, A. L. Crook, B. Curtin, D. M. Debroy, A. Del Toro Barba, S. Demura, A. Dunsworth, D. Eppens, C. Erickson, L. Faoro, E. Farhi, R. Fatemi, L. Flores Burgos, E. Forati, A. G. Fowler, B. Foxen, W. Giang, C. Gidney, D. Gilboa, M. Giustina, A. Grajales Dau, J. A. Gross, S. Habegger, M. C. Hamilton, M. P. Harrigan, S. D. Harrington, M. Hoffmann, S. Hong, T. Huang, A. Huff, W. J. Huggins, S. V. Isakov, J. Iveland, E. Jeffrey, Z. Jiang, C. Jones, P. Juhas, D. Kafri, T. Khattar, M. Khezri, M. Kieferová, S. Kim, A. Y. Kitaev, P. V. Klimov, A. R. Klots, A. N. Korotkov, F. Kostritsa, J. M. Kreikebaum, D. Landhuis, P. Laptev, K.-M. Lau, L. Laws, J. Lee, K. W. Lee, B. J. Lester, A. T. Lill, W. Liu, A. Locharla, F. Malone, O. Martin, J. R. McClean, M. McEwen, B. Meurer Costa, K. C. Miao, M. Mohseni, S. Montazeri, E. Mount, W. Mruczkiewicz, O. Naaman, M. Neeley, A. Nersisyan, M. Newman, A. Nguyen, M. Nguyen, M. Y. Niu, T. E. O’Brien, R. Olenewa, A. Opremcak, R. Potter, C. Quintana, N. C. Rubin, N. Saei, D. Sank, K. Sankaragomathi, K. J. Satzinger, H. F. Schurkus, C. Schuster, M. J. Shearn, A. Shorter, V. Shvarts, J. Skruzny, W. C. Smith, D. Strain, G. Sterling, Y. Su, M. Szalay, A. Torres, G. Vidal, B. Villalonga, C. Vollgraff-Heidweiller, T. White, C. Xing, Z. Yao, P. Yeh, J. Yoo, A. Zalcman, Y. Zhang, N. Zhu, H. Neven, D. Bacon, J. Hilton, E. Lucero, R. Babbush, S. Boixo, A. Megrant, J. Kelly, Y. Chen, V. Smelyanskiy, I. Aleiner, L. B. Ioffe and P. Roushan, 7 December 2022, Nature.
DOI: 10.1038/s41586-022-05348-y