As you know, we are at this time of the year when the new RAM standard has been released, and it’s DDR5. This announcement has caught the eyes of both enthusiasts and professionals alike. 6 years ago, the DDR4 standard was launched, and many made the switch in less than 2 years. The new DDR5 RAM promises double the performance than current DDR4 modules, while lowering power consumption.
DDR5 features

Clock Speeds
The latest generation of DDR(Double Data Rate) memory gets a speed bump. The older DDR4 had an average clock speed of 3200MHz, but DDR5 has an average clock speed of 4800MHz, and goes all the way to 6400MHz.
Capacity
With the new DDR5 buffer chip DIMMs(Dual In-line Memory Modules), you can use densities of up to 64-Gb DRAMs in a single-die package while DDR4 peaks out at 16 Gb DRAM in a single-die package. DDR5 supports features like on-die ECC, error transparency mode, post-package repair, and read and write CRC modes to support higher-capacity DRAMs.
Transfers per second
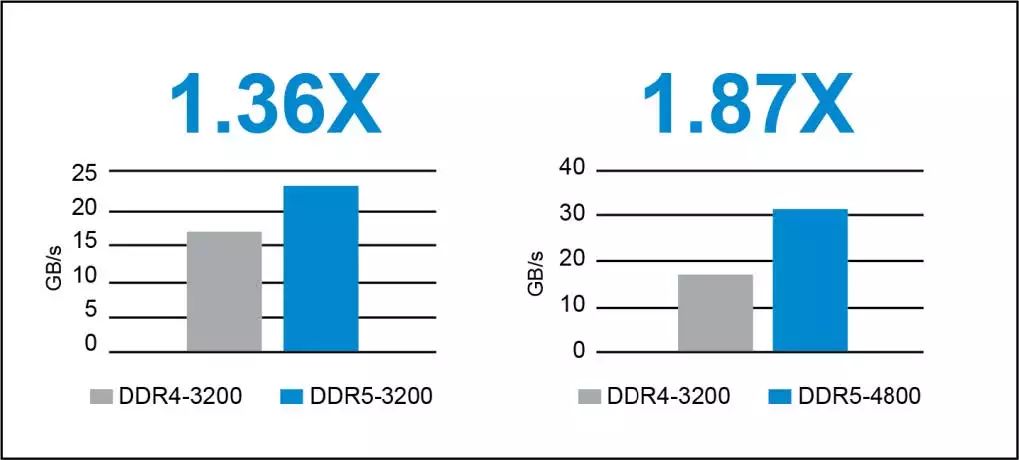
Most enthusiasts are always short of memory bandwidth. With DDR5, you can fill your unquenchable need for speed. Current DDR4 DIMMs top out at 3200 MT/s (Mega Transfers Per Second) with a clock rate of 1.6GHz, while the next-gen DDR5 DIMMs peak at a staggering 6400 MT/s while initial designs will average at 4800 MT/s
Lower Voltage
A major change in DDR4 to DDR5 is the operating voltage(VDD). This translates to lower power. The buffer chip and DRAM Registering Clock Driver(RCD) voltage is dropped by 100mv to 1.1v from 1.2v
Power Architecture
With the latest DDR5 DIMMs, power management is now on the DIMM itself, and not on the motherboard any more. The DIMMs now get a 12v power management IC (PMIC) for better system power loading. The PMIC now distributes the 1.1v VDD helping the DIMM attain better control of the power supply.
Channel Architecture
Another major change in the architecture is the channels. DDR4 DIMMs have a 72-bit bus, comprised of 64 data bits plus 8 ECC bits. But with DDR5, there are 2 channels and each channel is 40 bits wide, consisting of 32 data bits with 8 ECC bits. While the data width is the same (a total of 64 bits), having 2 smaller independent channels improves memory access efficiency. So eventually, you not only get a speed increase, you also get double the efficiency.
In the DDR5 DIMM architecture, the left and right side of the DIMM, each served by an independent 40-bit wide channel, share the RCD. In DDR4, the RCD provides two output clocks per side. In DDR5, the RCD provides four output clocks per side. The 32-bit data of each 40-bit channel consist of four 8-bit lanes, and each of these lanes gets an independent clock signal from the RCD. Giving each lane an independent clock improves signal integrity, helping to address the lower noise margin issue raised by lowering the VDD.
Burst Length
DDR4 burst chop length is four and burst length is eight, whereas in DDR5, the burst chop and burst length is increased to eight and sixteen to increase burst payload. Burst length of 16(BL16) allows a single burst to access 64 Bytes of data, which is the normal CPU cache line size. This can be done with just one of the two independent channels and thus provides greater memory efficiency.
Bank Groups
DDR5 also doubles the number of bank groups (BGs) compared to DDR4, while keeping the number of banks per BG the same. This means that the total number of banks will be double that of DDR4. This helps controllers avoid performance degradation associated with sequential memory accesses within the same bank. All of these features and more point to how significant of an upgrade DDR5 will be compared to DDR4.
The need for DDR5 RAM
Ever since AMD launched their Ryzen processors in 2017, the core war began. AMD started manufacturing quad core 8 threaded processors for the midrange market whereas the upper midrange market got hold of the 16 core and 32 thread processors codenamed “Threadripper”. With every iteration, AMD was improving their processors, and fighting the core war against Intel. Due to this, Intel was forced to respond with increasing the core count on their CPUs, but they haven’t been very aggressive.
Within a span of three years, AMD went from just 4 cores in a single gaming computer, to around 4 times the amount of cores today. That’s a huge leap for AMD. So as cores increase, the memory bandwidth per core needs to increase too. This is where DDR5 RAM comes in.
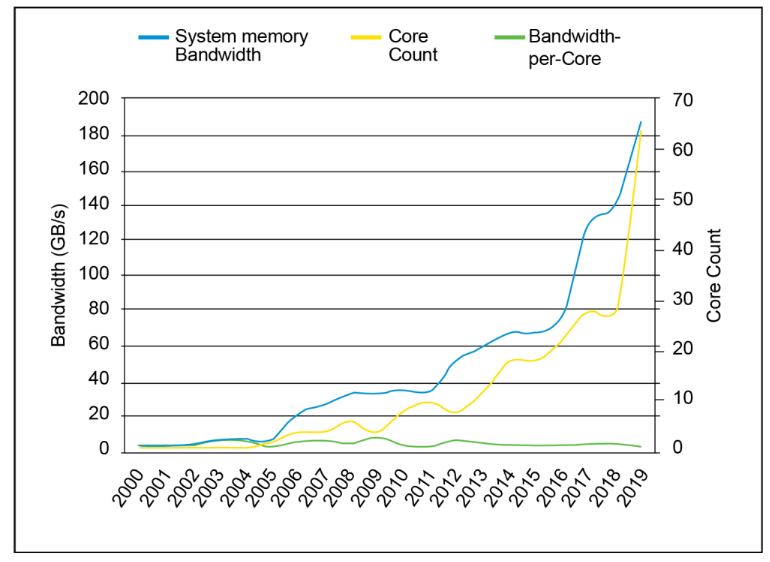
As we can see from Micron’s chart above, bandwidth per core has remained relatively stable since the early 2000s. However, bandwidth per core has started to decline since last year.
DDR5 Cost
At first, DDR5 will be a bit expensive due to the new standard, but eventually, the prices will hit rock bottom in a span of 3 to 5 years per GB. Back then for PC builders, RAM has always been one of the more inexpensive components. But recent DRAM shortages have resulted in price increases that have hung around for quite some time. But once DDR5 becomes widespread, users will be able to save money even if they somehow find themselves needing 8 or 16 GigaBytes of RAM. Also, RAM frequencies were kind of overlooked for a long time by PC enthusiasts simply because they didn’t give tangible performance gains in many applications. More particularly in games. That changed when AMD came into the picture.
Performance benefits on AMD systems
While many users of Intel systems barely need fast RAM, the ones on AMD systems completely do. Ryzen processors perform way better when paired with higher clocked RAM, and you can see the performance gains when overclocking them. Ryzen CPU’s noticeable frame rate increases can be seen in certain titles when you pair them with faster RAM and a high-end discrete graphics card as shown in the video below.
While DDR5 speeds are expected to max out at 6400MHz, SK Hynix has promised DDR5 kits at 8400MHz. This will be an amazing improvement when compared to the 3200MHz DDR4 RAM currently used in gaming builds today. The high speeds will also help users who game on integrated graphics (iGPU) that leverage main system memory as VRAM. Hence budget laptop users can also rejoice. The improved bandwidth will also be of great importance in cloud and server applications.
DDR5 Availability
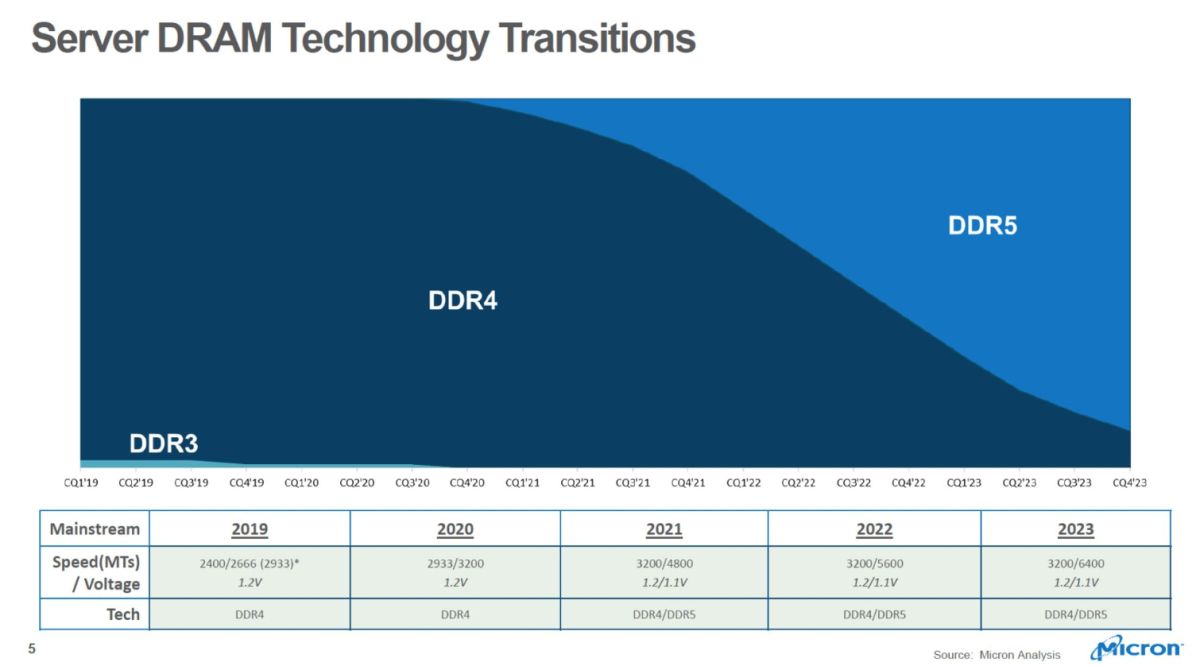
At the earliest, we could see server grade DDR5 memory kits at the end of this year (2020), and will mainly be for enterprise grade applications. The consumer version of DDR5 will finally hit the market by late 2021. Samsung, Micron and SK Hynix are developing modules, and should hopefully be ready by 2021 or 2022 latest. A solid indicator of when DDR5 is going to become fully mainstream has been displayed in the chart given below designed by SK Hynix. They’ve tried to estimate how the sales market will be split in the coming years.
Will DDR5 be worth it in the long run?
It would be too early to say that due to them not being launched yet. But with AMD releasing their Zen 4 CPUs next year(Ryzen 5000 series), they will be using a new socket (might use the new AM5 chipset), and will have full fledged support for DDR5. This will boost DDR5 production, and will cause a humongous demand for DDR5. It’s not just AMD, but Intel too will be pairing the new DIMMs with their Adler Lake.
So eventually as they churn out more DIMMs we should see the performance difference, the gains, the endurance over long periods of time, and then draw up an estimate of how well DDR5 will work. That’s when you will know if DDR5 is worth it in the long run. For the time being, DDR4 is great as ever!