Lead Image: Microplastics are tiny particles of plastic that are smaller than 5mm in size and are found in the environment, including in water sources. These particles can come from a variety of sources, including the breakdown of larger plastic items, the use of microbeads in personal care products, and the release of plastic fibers during the washing of synthetic clothing. Microplastics have been found in tap water, bottled water, and even in the oceans, and their presence in the environment is a cause for concern as they can be ingested by marine life and potentially enter the food chain.
Princeton Engineering researchers have developed a cost-effective way to use breakfast foods to create a material that can remove salt and microplastics from seawater.
The researchers used egg whites to create an aerogel, a versatile material known for its light weight and porosity. It has a range of uses, including water filtration, energy storage, and sound and thermal insulation. Craig Arnold, the Susan Dod Brown Professor of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering and vice dean of innovation at Princeton, leads a lab that focuses on creating new materials, including aerogels, for engineering purposes.
One day, sitting in a faculty meeting, he had an idea.
“I was sitting there, staring at the bread in my sandwich,” said Arnold. “And I thought to myself, this is exactly the kind of structure that we need.” So he asked his lab group to make different bread recipes mixed with carbon to see if they could recreate the aerogel structure he was looking for. None of them worked quite right initially, so the team kept eliminating ingredients as they tested, until eventually, only egg whites remained.
“We started with a more complex system,” Arnold said, “and we just kept reducing, reducing, reducing, until we got down to the core of what it was. It was the proteins in the egg whites that were leading to the structures that we needed.”
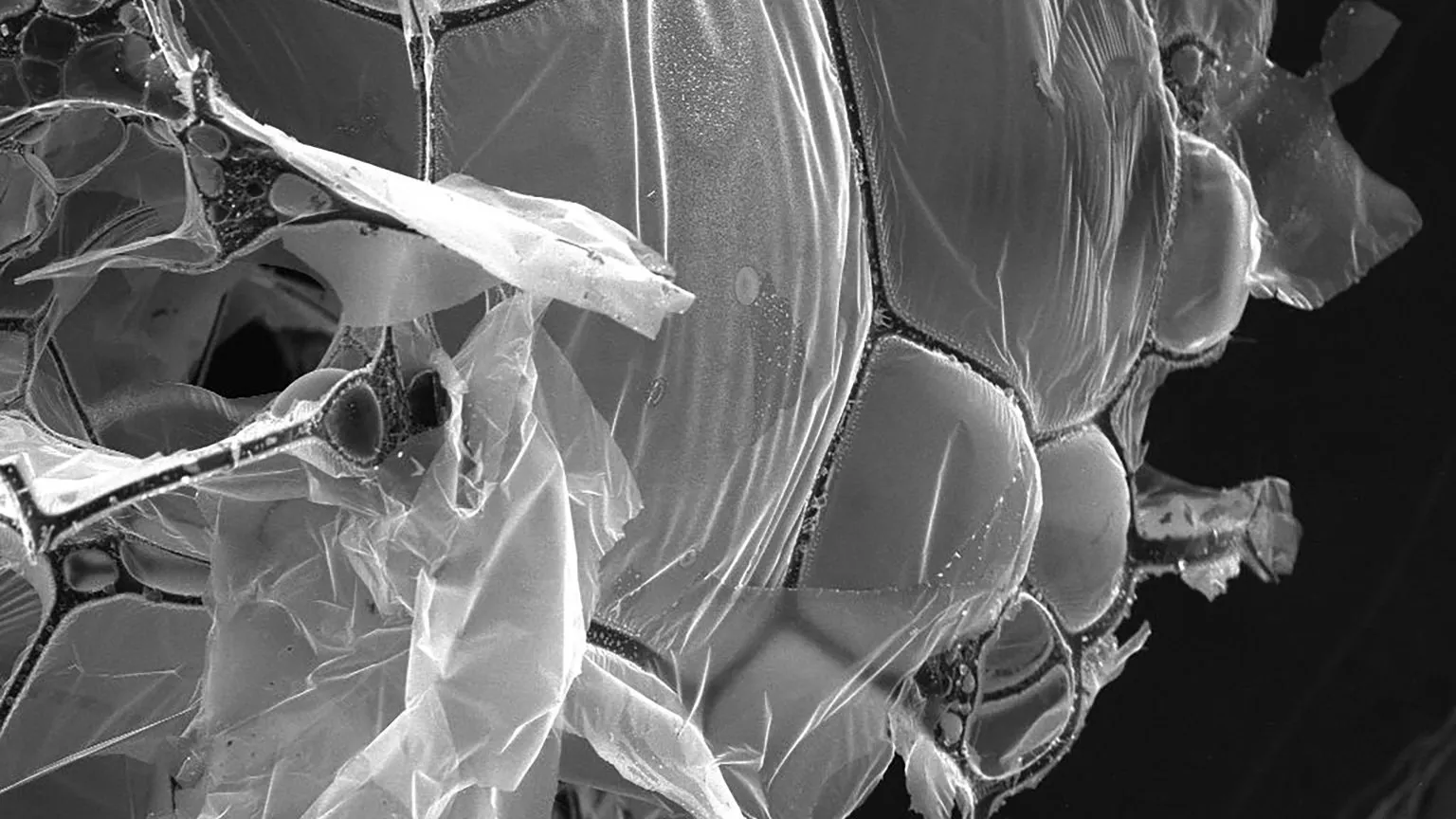
Egg whites are a complex system of almost pure protein that — when freeze-dried and heated to 900 degrees Celsius in an environment without oxygen — create a structure of interconnected strands of carbon fibers and sheets of graphene. In a paper published Aug. 24 in Materials Today, Arnold and his coauthors showed that the resulting material can remove salt and microplastics from seawater with 98% and 99% efficiency, respectively.
“The egg whites even worked if they were fried on the stove first, or whipped,” said Sehmus Ozden, the first author of the paper. Ozden is a former postdoctoral research associate at the Princeton Center for Complex Materials and is now a scientist at Aramco Research Center. While regular store-bought egg whites were used in initial tests, Ozden said, other similar commercially available proteins produced the same results.
“Eggs are cool because we can all connect to them and they are easy to get, but you want to be careful about competing against the food cycle,” said Arnold. Because other proteins also worked, the material can potentially be produced in large quantities relatively cheaply and without impacting the food supply. One next step for the researchers, Ozden noted, is refining the fabrication process so it can be used in water purification on a larger scale.
If this challenge can be solved, the material has significant benefits because it is inexpensive to produce, energy-efficient to use, and highly effective. “Activated carbon is one of the cheapest materials used for water purification. We compared our results with activated carbon, and it’s much better,” said Ozden. Compared with reverse osmosis, which requires significant energy input and excess water for operation, this filtration process requires only gravity to operate and wastes no water.
While Arnold sees water purity as a “major grand challenge,” that is not the only potential application for this material. He is also exploring other uses related to energy storage and insulation.
Reference: “Egg protein derived ultralightweight hybrid monolithic aerogel for water purification” by Sehmus Ozden, Susanna Monti, Valentina Tozzini, Nikita S. Dutta, Stefania Gili, Nick Caggiano, A. James Link, Nicola M. Pugno, John Higgins, Rodney D. Priestley and Craig B. Arnold, 24 August 2022, Materials Today.
DOI: 10.1016/j.mattod.2022.08.001
The research included contributions from the departments of chemical and biological engineering and geosciences at Princeton and elsewhere. “It’s one thing to make something in the lab,” said Arnold, “and it’s another thing to understand why and how.” Collaborators who helped answer the why and how questions included professors Rodney Priestley and A. James Link from chemical and biological engineering, who helped identify the transformation mechanism of the egg white proteins at the molecular level. Princeton colleagues in geosciences assisted with measurements of water filtration.
Susanna Monti of the Institute for Chemistry of Organometallic Compounds and Valentina Tozzi from Instituto Nanoscienze and NEST-Scuola Normale Superiore created the theoretical simulations that revealed the transformation of egg white proteins into the aerogel.
The study was funded by the Princeton Center for Complex Materials and the National Science Foundation