Latest Articles
-
Feb- 2022 -7 FebruaryArcheology

Comet’s Devastating Explosion Over North America 1,500 Years Ago Caused Extensive Destruction
Did comet’s fiery destruction lead to downfall of ancient Hopewell? Researchers at the University of Cincinnati find evidence of cosmic cataclysm 1,500 years ago at 11 ancient sites. The rapid decline of the Hopewell culture about 1,500 years ago might be explained by falling debris from a near-Earth comet that created a devastating explosion over North America, laying waste to forests and Native American villages alike. Researchers with the University of Cincinnati found evidence of a cosmic airburst at 11 Hopewell archaeological sites in three states stretching across the Ohio River Valley. This was home to the Ohio Hopewell, part…
Read More » -
5 FebruaryQuantum Computing
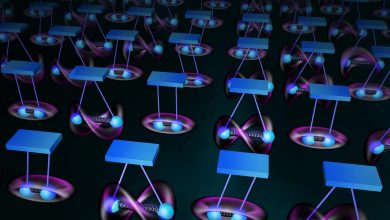
MIT Physicists Have Discovered New Qubits for Quantum Computers Using Vibrating Atoms
MIT researchers have found a way to store quantum information in the vibrational motion of atom pairs, similar to the swinging motion of two pendula, connected by a spring. The quantum register contains hundreds of pairs of vibrating qubits that researchers can coherently control for over ten seconds. Credit: Sampson Wilcox/RLE The new qubits stay in “superposition” for up to 10 seconds, and could make a promising foundation for quantum computers. MIT physicists have discovered a new quantum bit, or “qubit,” in the form of vibrating pairs of atoms known as fermions. They found that when pairs of fermions are…
Read More » -
4 FebruaryDNA

Are Scientists Being Fooled by Bacteria? New Machine Learning Algorithm Reveals the Truth About DNA
Previous studies of a genetic on/off switch may have been confounded by contamination, but Mount Sinai scientists have created a new tool for accurately determining whether it plays a role in human disease. For decades, a small group of cutting-edge medical researchers have been studying a biochemical, DNA tagging system, which switches genes on or off. Many have studied it in bacteria and now some have seen signs of it in, plants, flies, and even human brain tumors. However, according to a new study by researchers at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, there may be a hitch:…
Read More » -
4 FebruaryMolecular Biology

New Mosquito Vision Discovery Could Help You Hide From These Disease-Carrying Bloodsuckers
Mosquitoes are seeing red: These new findings about their vision could help you hide from these disease vectors. Beating the bite of mosquitoes this spring and summer could hinge on your attire and your skin. New research led by scientists at the University of Washington indicates that a common mosquito species — after detecting a telltale gas that we exhale — flies toward specific colors, including red, orange, black and cyan. The mosquitoes ignore other colors, such as green, purple, blue, and white. The researchers believe these findings help explain how mosquitoes find hosts, since human skin, regardless of overall…
Read More » -
4 FebruaryMaterials Science
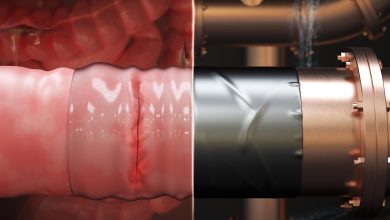
MIT Engineers Develop Biocompatible Surgical “Duct Tape” as an Alternative to Sutures
Lead Image: A new MIT-designed surgical sticky tape can be applied quickly and easily, like duct tape to a pipe, to repair leaks and tears in the gastrointestinal tract and other tissues and organs. Credit: Courtesy of the researchers The sticky patch could be quickly applied to repair gut leaks and tears. A staple on any engineer’s workbench, duct tape is a quick and dependable fix for cracks and tears in many structural materials. MIT engineers have now developed a kind of surgical duct tape — a strong, flexible, and biocompatible sticky patch that can be easily and quickly applied…
Read More »