Latest Articles
-
Sep- 2022 -8 SeptemberNutrition

Three Amazing Caffeine Alternatives for Quick, Clean Energy – And the Science Behind Them
If you’re anything like the vast majority of Americans, you’ve probably consumed caffeine nearly every day of your adult life. The question is, do you do it because you like it, or because you need it? In a March 2022 survey carried out by the International Food Information Council (IFIC), respondents over the age of 65 generally said they drink caffeinated beverages because they enjoy the flavor, while under-45s were more likely to report taking caffeine solely for its well-known benefits as a stimulant.[1] But these benefits are part of a trade-off that might not be worth it if you…
Read More » -
7 SeptemberNeuroscience

Scientists Discover a Surprising Culprit Worsens Stroke
A stroke occurs when a blood vessel in the brain bursts or when something stops the flow of blood to a certain region of the brain. Neuroscientists make a surprising brain discovery. According to research, a set of amino acids that normally maintain brain function play a crucial role in the brain deterioration that could occur after a stroke or traumatic brain injury. According to Dr. Sergei Kirov, a neuroscientist in the Department of Neuroscience and Regenerative Medicine at the Medical College of Georgia, the new study for the first time provides surprising evidence that four common nonexcitatory amino acids, which…
Read More » -
6 SeptemberGaming

E-Sports Offers New Opportunities Not Only For Players
Esports fans believe that esports has appeared relatively recently. However, in reality, computer game competitions began in 1972. In some countries, the attitude towards esports has changed in recent years. So, earlier in India, it was more associated with a “fake sport” or online entertainment. After the Asian Games 2022, the skeptics abandoned the above statements. Esports tournaments are attractive because they allow fans to enjoy immersive games. At the same time, esports tournaments became super-popular with betting fans, because they offer fast engagement and almost round-the-clock availability. Many perceive esports as somewhat stereotypical: young people play for a lot…
Read More » -
4 SeptemberCOVID-19
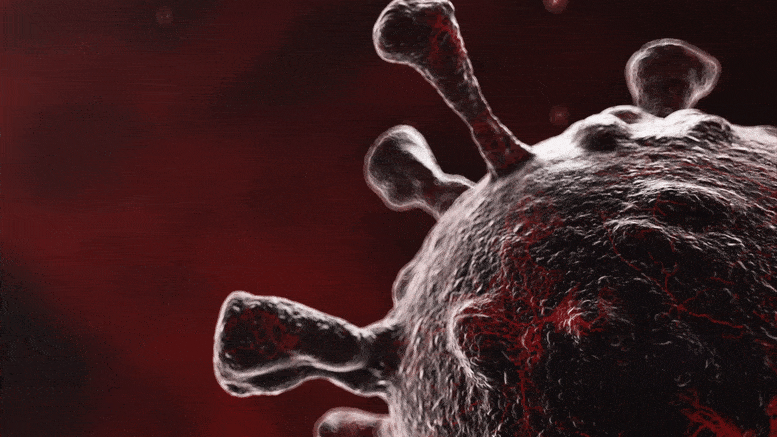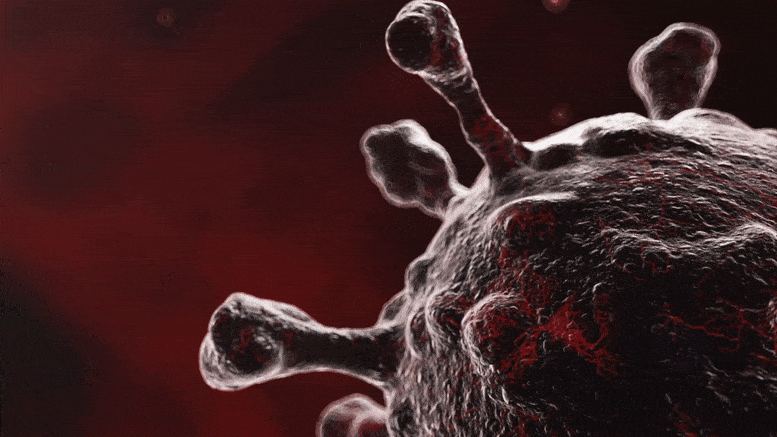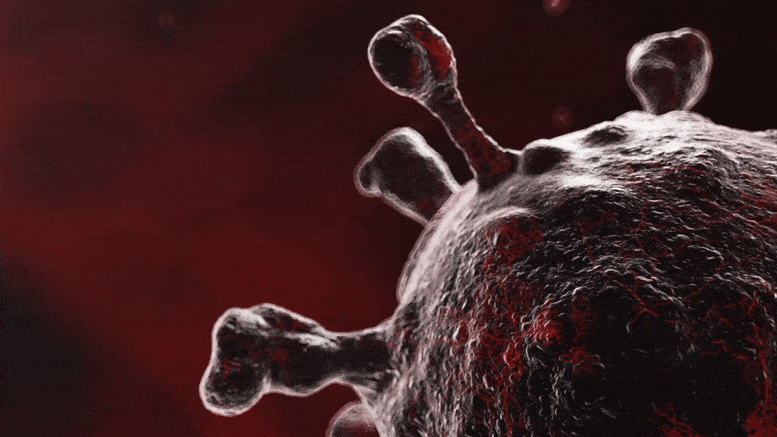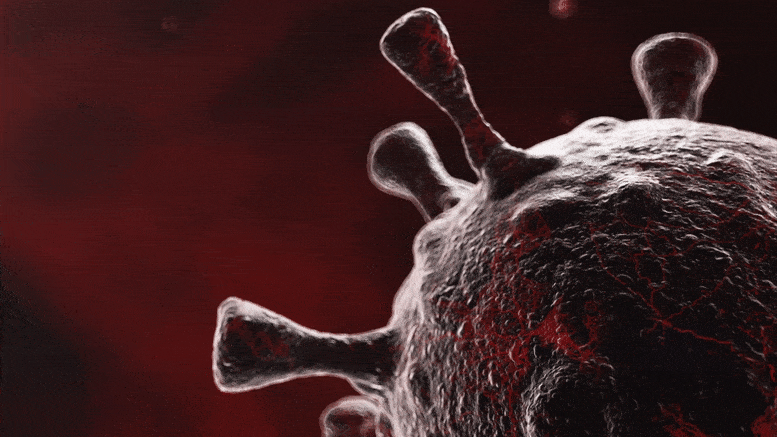
Why Is Omicron More Infectious Than Other COVID-19 Variants?
Lead image: The Omicron variant of SARS-CoV-2 spreads more easily than the other main variants but also causes less severe illness and death. Researchers discovered which mutations of the Omicron SARS-CoV-2 virus make it more efficient at infecting cells and evading antibodies by using virus-like particles. As the Omicron variant of SARS-CoV-2 quickly spread throughout the world earlier this year, researchers from Gladstone Institutes, the University of California Berkeley, and the Innovative Genomics Institute utilized virus-like particles to determine which elements of the virus are responsible for its heightened infectivity and transmission. Additionally, they demonstrated that although antibodies produced against…
Read More » -
3 SeptemberNASA
“Solar Clock” Can Predict Dangerous Solar Flares Years in Advance
Lead Image: Solar flares – like this one captured by a NASA satellite orbiting the Sun – eject huge amounts of radiation. Credit: NASA Important solar cycle landmarks that are influenced by variations in the sun’s magnetic field might predict changes in weather patterns and risks to telecommunications. We have been attempting to define the solar cycle using sunspots ever since humanity was able to notice them for the first time around 400 years ago. Solar activity, including sunspots and solar flares, ebbs and flows about every 11 years, changing Earth’s weather patterns and sometimes posing a hazard to communications.…
Read More »