Latest Articles
-
May- 2022 -4 MayAstronomy
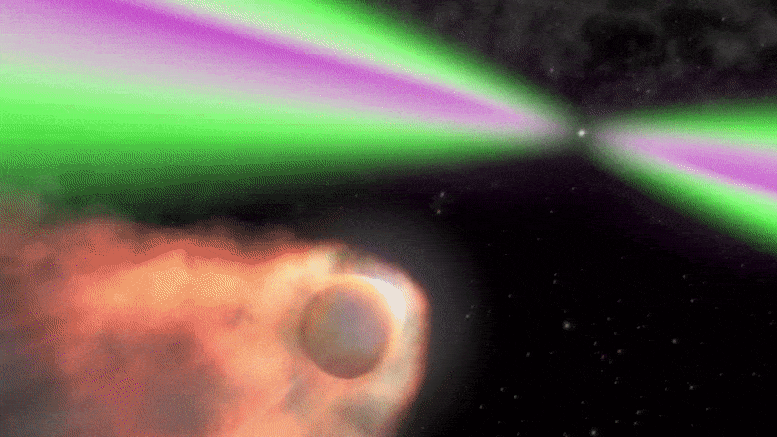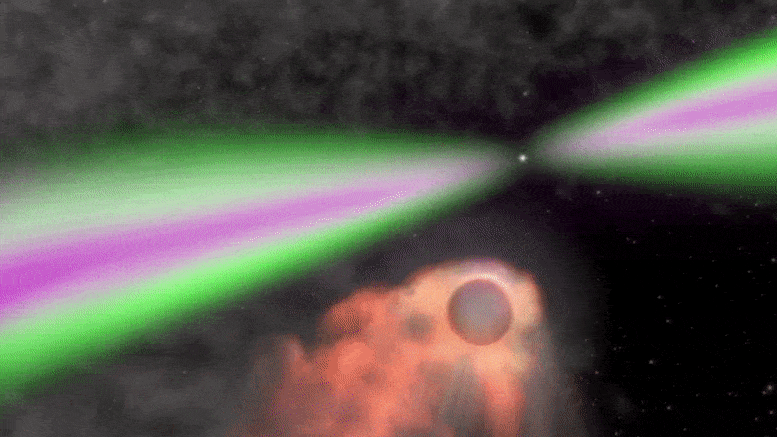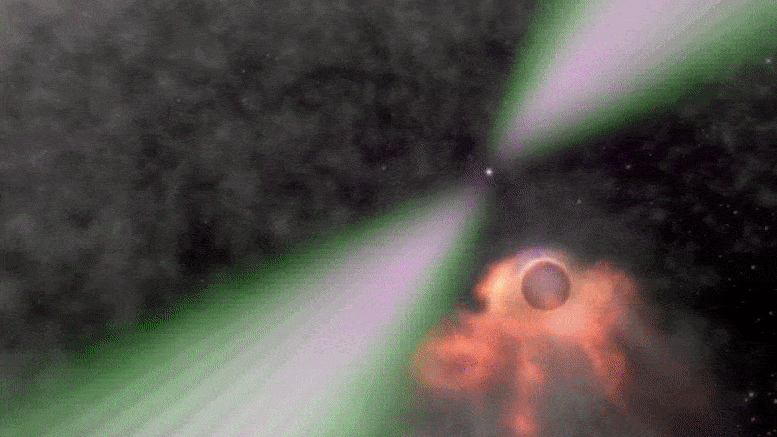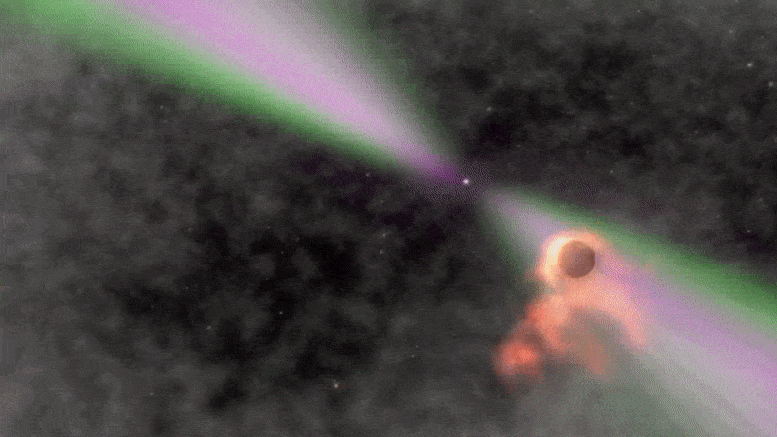
MIT Astronomers Discover Mysterious “Black Widow” Binary System
Animation depicting a black widow pulsar and its small stellar companion. Credit: NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center/Cruz deWilde The system, which may have originated near the center of the Milky Way, is orbited by a third stellar companion. The flashing of a nearby star has drawn MIT astronomers to a new and mysterious system 3,000 light-years from Earth. The strange stellar oddity appears to be a new “black widow binary” — a rapidly spinning neutron star, or pulsar, that is circling and slowly consuming a smaller companion star, as its arachnid namesake does to its mate. There are about two…
Read More » -
3 MayMolecular Biology
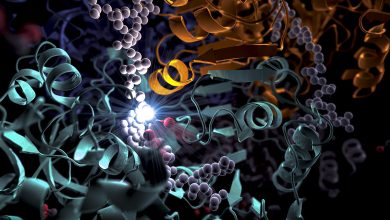
Bacterial Enzyme Converts CO2 Into Carbon Compounds 20x Faster Than Photosynthesis
Lead Image: Artist interpretation of the enzyme Credit: SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory Researchers discover that a spot of molecular glue and a timely twist help a bacterial enzyme convert carbon dioxide into carbon compounds 20 times faster than plant enzymes do during photosynthesis. The results stand to accelerate progress toward converting carbon dioxide into a variety of products. Carbon fixation, or the conversion of carbon dioxide from the air into carbon-rich biomolecules, is essential for plants’ survival. That’s the whole point of photosynthesis, and a cornerstone of the vast interlocking system that cycles carbon through plants, animals, microbes, and the…
Read More » -
2 MayQuantum Computing

Quantum Future: Developing the Next Generation of Quantum Algorithms and Materials
Lead Image: Quantum computers are especially adept at simultaneously considering large numbers of possible combinations, but the instability of qubits in modern devices contributes to errors in calculations. Credit: Image by Timothy Holland | Pacific Northwest National Laboratory Simulating a Quantum Future Quantum computers are anticipated to revolutionize the way researchers address complex computing problems. These computers are being developed to address major challenges in fundamental scientific fields such as quantum chemistry. In its present state of development, quantum computing is very susceptible to noise and disruptive influences in the environment. This makes quantum computers “noisy,” since quantum bits, or…
Read More » -
1 MayClimate Change
Filling the Climate Change Data Gap: Amazon Rainforest Gases Affect the Earth’s Atmosphere
Findings may fill gap for climate change, atmospheric research beyond tropical regions. According to a new study by scientists at Pacific Northwest National Laboratory (PNNL), plant-foliage-derived gases generate a previously unknown atmospheric phenomenon over the Amazon rainforest. The discovery has significant implications for atmospheric science and climate change modeling. “The tropical Amazon rainforest constitutes the lungs of the Earth, and this study connects natural processes in the forest to aerosols, clouds, and the Earth’s radiative balance in ways that have not been previously recognized,” said Manish Shrivastava, PNNL Earth scientist and primary investigator of the study. The research was recently…
Read More » -
1 MayAstronomy

Instability at the Beginning of the Solar System – Implications for Mysterious “Planet 9”
Lead Image: All stars, including our sun, are born from a cloud of dust and gas. This cloud can also seed planets that will orbit the star. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech The Instability at the Beginning of the Solar System A new explanation for why our solar system is the way it is — and why others are, too. Seth Jacobson of Michigan State University and colleagues in China and France have unveiled a new theory that could help solve a galactic mystery of how our solar system evolved. Specifically, how did the gas giants — Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune —…
Read More »