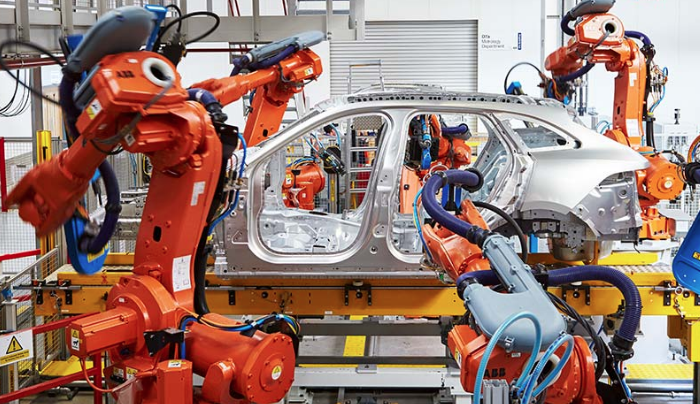
Robots are not the future of the workplace. They are the present. Many companies have already integrated intelligent and highly-efficient machines to work in offices, factories, and on the ground. They are still far from taking over jobs, which many fears will happen, but automation has already improved processes and productivity.
Right now, a significant transformation is happening. The first industrial revolution saw mechanization through water and steam power. Electricity triggered a significant change and advancement in the second industrial revolution. In the third industrial revolution, computers and automation were adopted.
The world has arrived at the fourth industrial revolution. The Industry 4.0 definition states that, in addition to the integration of computers and automation, uses smart and autonomous systems. These technologies are driven by massive amounts of data that is fed to machine learning models.
Here are the companies that have already employed intelligent and highly-efficient robots in manufacturing.
Adidas
A few years ago, the German athleisure brand Adidas announced plans to open high-tech factories in its home country, Germany, and the United States. Called Speedfactory, the facilities were heavily reliant on technologies to create and assemble running shoes. The factory used robotic arms, computerized knitting machines, and a three-dimensional printer. There were still human workers in these facilities, but they aid, instead of lead, the production.
Speedfactory was a response to the high demand for running shoes in the U.S., Europe, and around the world. Prior to its establishment, Adidas was manufacturing its products in Asia, including China, Vietnam, and Indonesia. However, they needed to make more and, because of the rising cost of labor in the region, they wanted a solution that would make them eventually less dependent on overseas factories.
Adidas had big plans for Speedfactory but, in 2019, the company decided to shut down the facilities.
Bosch
Bosch, another company born and based in Germany, is also leading the pack in embracing Industry 4.0. The Bosch Automotive Diesel System factory located in China integrates machinery, big data, and IIoT (Industry Internet of Things) to improve operations.
The machines used in production are all connected in order to monitor and assure that everything is working properly. Each machine is embedded with sensors that collect troves of data and immediately detect if there is a bottleneck in production.
Humans are still around, but they are present to respond if the machines found a problem. The machines can also foresee when a failure is imminent, allowing human workers to perform maintenance to prevent any damages from occurring in the future.
Whirlpool
Whirlpool had an important goal when it started integrating new technologies into its production line: to eliminate waste. To help them achieve this goal, the home appliance manufacturer implemented an analytics platform that can calculate accurately the amount of waste a facility generates, make adjustments, and provide recommendations to reduce excesses.
During the pandemic, Whirlpool also unlocked more benefits to using smart and autonomous robots. Instead of having a factory full of human workers, which can increase the risk of transmission, its facilities were able to protect its own employees without disrupting production by having highly-efficient machines working in the factories, ensuring social distancing among humans.
The company also used augmented reality, as a substitute for human trainers, to train new employees and design a workstation that follows all the measures required to prevent COVID-19.
Amazon
Amazon, one of the largest e-commerce platforms around the world, is using technology in its warehouses. This does not really come as a surprise. Its facilities are massive and the company needs to fulfill countless numbers of orders quickly and accurately. The company founded by billionaire Jeff Bezos has also been experimenting with technology, including robots and drones for delivery, regularly.
In Amazon’s warehouses, different robots are working alongside humans. Orange machines in wheels are fetching packages and delivering them to the correct chute, ready to be loaded in a truck for delivery. Robots are also grabbing boxes from storage and handling them to a human co-worker waiting below.
The system running in warehouses ofAmazon is incredibly complex and impressive. The movements of robots are overseen by the cloud which acts similar to air traffic control, coordinating individual routes so that no machines collide on the warehouse floor.
Technology is already changing manufacturing and warehouse work. It has made tasks easier, faster, more efficient, and, in many cases, safer for humans. Smart robots will continue to be integrated by more companies as they become more affordable and their benefits become more apparent.





