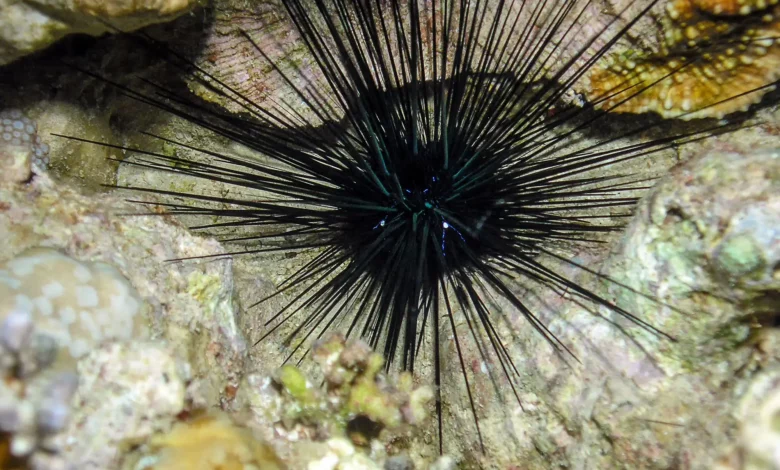

A scuticociliate, a single-celled organism, has been identified as the cause of the 2022 mass die-off of long-spined sea urchins in the Caribbean and Florida’s east coast. These urchins are crucial for coral reef health, and the discovery raises questions about the ciliate’s presence, growth conditions, and potential impact on other species. Photo of Long Spined Sea Urchin (Diadema antillarum).
The mass die-off of the long-spined sea urchin – a loss that threatens the health of coral reefs from the Caribbean to Florida’s east coast – was caused by a one-celled organism called a ciliate.
The search for the 2022 killer that decimated the long-spined sea urchin population in the Caribbean and along Florida’s east coast is over. A team of researchers organized by Mya Breitbart, Distinguished University Professor at the University of South Florida’s College of Marine Science, identified a single-celled organism called a ciliate as the cause of a massive die-off event to a marine animal vital to coral reef health.
Their findings were reported on April 19 in the journal Science Advances.
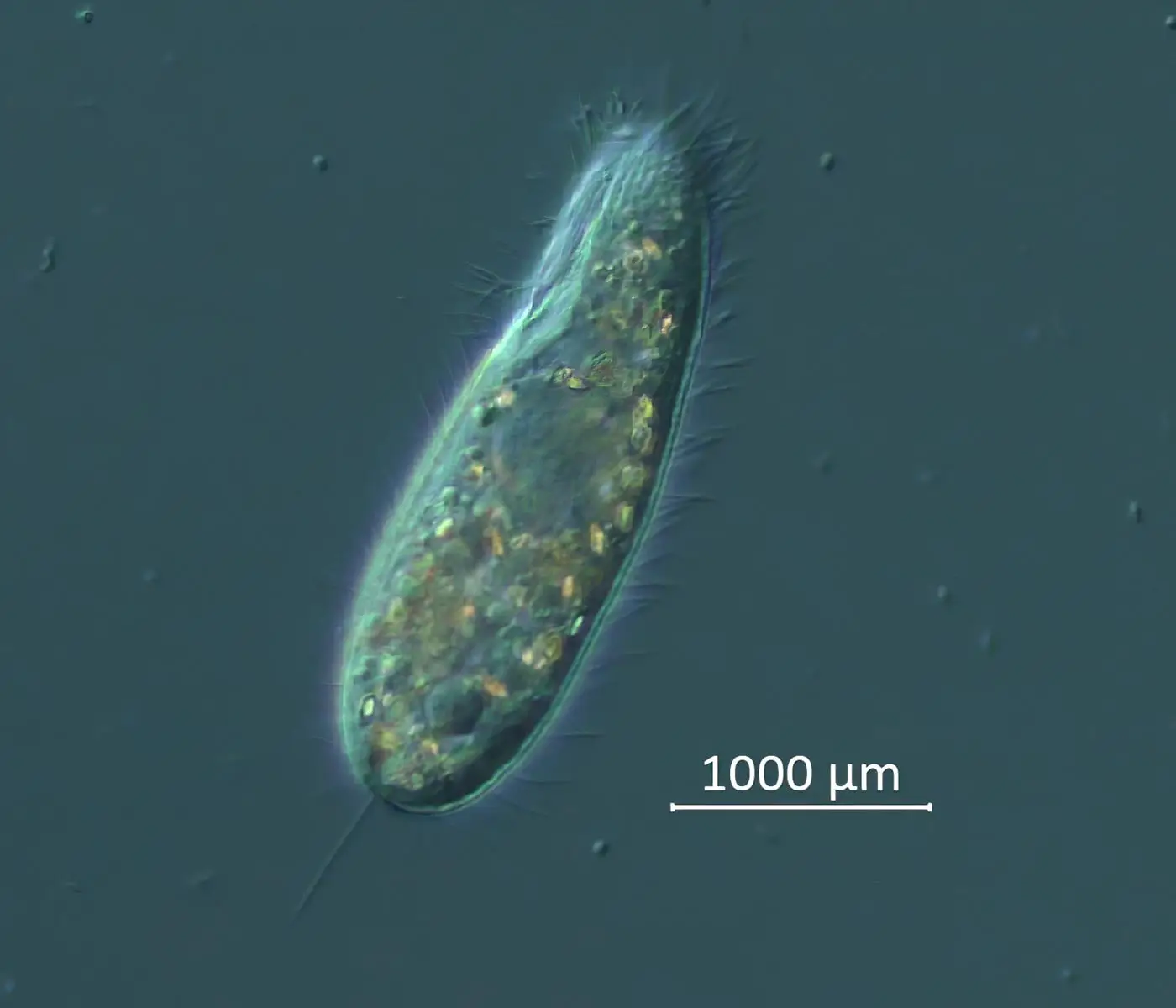
“We’re beyond thrilled to get to the bottom of the 2022 mystery and a bit stunned we did it so quickly,” said Breitbart, senior author on the Science Advances study and an expert in marine genomics. “We had a great team in place and the tools needed to do the ocean science equivalent of a forensic investigation.”
Ciliates are microscopic organisms covered in hair-like structures called cilia that help them move and eat. They are found almost anywhere there is water and most are not disease-causing agents. However, this specific species of ciliate – called a scuticociliate – has been implicated in die-offs of other marine species, such as sharks, in the past.

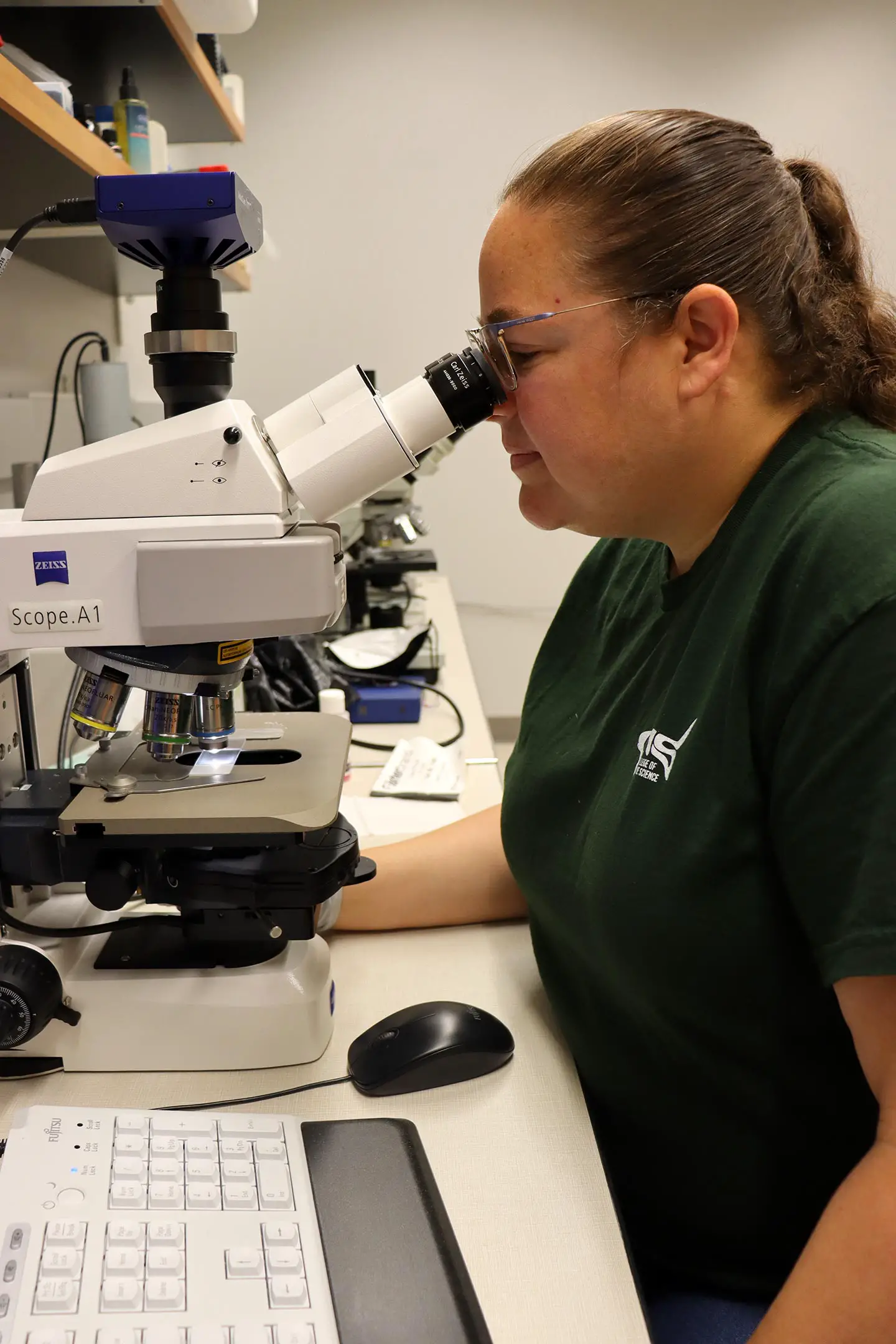
Examining urchins collected from 23 sites in the Caribbean, the research team used a series of techniques to confirm the source of the die-off event.
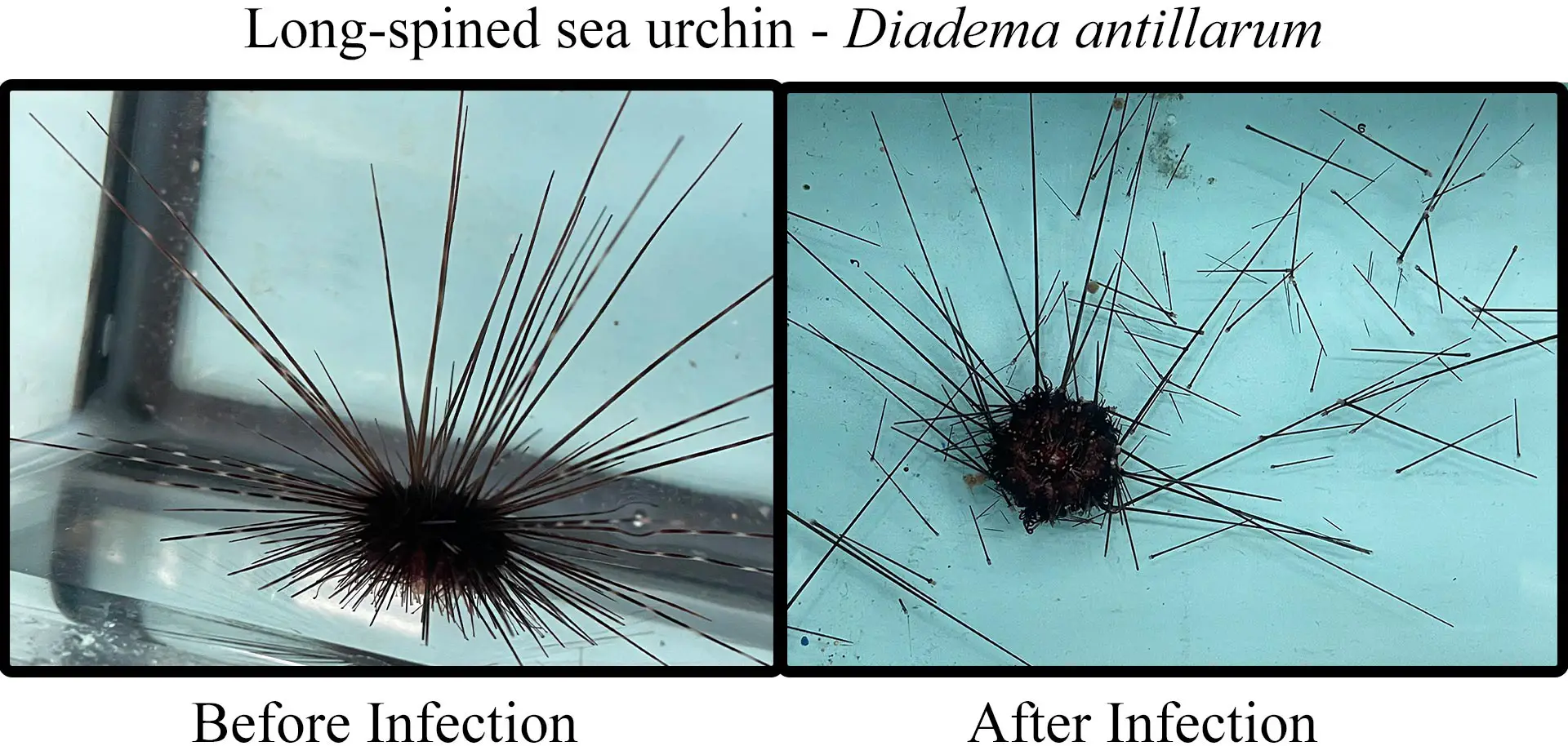
After identifying the ciliate in every affected urchin specimen using genomic techniques, the team grew ciliates in the lab and performed infection experiments at the USF College of Marine Science. When the pathogen was introduced to otherwise healthy urchins in an aquarium tank, the urchins died within a few days – replicating what was taking place in the ocean and confirming the ciliate as the disease source.

“We’re excited to share this information with everyone, from reef managers to additional scientists so we can explore it further and try to stop its spread,” Breitbart said.

The long-spined sea urchins inhabit shallow tropical waters and feed on algae that would otherwise destroy a reef. They began to lose their spines within days of contracting an unknown disease and died in droves starting in January 2022.
A similar die-off event took place in the early 1980s, which wiped out 98 percent of the long-spined sea urchin population. The culprit of that die-off remains a mystery.
Breitbart first got the call about the unfolding die-off at the end of March 2022. She immediately assembled a team consisting of Ian Hewson, lead author on the publication and a marine ecologist at Cornell University; Christina Kellogg, a microbiologist from the U.S. Geological Survey in St. Petersburg, Fla. who has worked extensively on coral reef diseases; and USF graduate student Isabella Ritchie.
“At the time, we didn’t know if this die-off was caused by pollution, stress, something else – we just didn’t know,” said Hewson, an expert in diseases that cause mass die-offs of sea stars, who flew from New York to the Caribbean Islands to observe the situation.
Even with the source of the mysterious die-off uncovered, questions still remain. For example:
- Is this ciliate new to the area, or was it there prior to the die-off?
- If it has been there, what environmental conditions favored its growth and why did it infect the urchins?
- Can it affect other species of urchins?
“One theory we have is that the ciliate grew well under high-productivity conditions that were observed in the Caribbean when the die-off first started,” Kellogg said. “We’re also curious about the fact that there is some overlap in some geographic areas where this die-off occurred and where corals are declining from stony coral tissue loss disease.”
Reference: “A scuticociliate causes mass mortality of Diadema antillarum in the Caribbean Sea” by Ian Hewson, Isabella T. Ritchie, James S. Evans, Ashley Altera, Donald Behringer, Erin Bowman, Marilyn Brandt, Kayla A. Budd, Ruleo A. Camacho, Tomas O. Cornwell, Peter D. Countway, Aldo Croquer, Gabriel A. Delgado, Christopher DeRito, Elizabeth Duermit-Moreau, Ruth Francis-Floyd, Samuel Gittens, Leslie Henderson, Alwin Hylkema, Christina A. Kellogg, Yasunari Kiryu, Kimani A. Kitson-Walters, Patricia Kramer, Judith C. Lang, Harilaos Lessios, Lauren Liddy, David Marancik, Stephen Nimrod, Joshua T. Patterson, Marit Pistor, Isabel C. Romero, Rita Sellares-Blasco, Moriah L. B. Sevier, William C. Sharp, Matthew Souza, Andreina Valdez-Trinidad, Marijn van der Laan, Brayan Vilanova-Cuevas, Maria Villalpando, Sarah D. Von Hoene, Matthew Warham, Tom Wijers, Stacey M. Williams, Thierry M. Work, Roy P. Yanong, Someira Zambrano, Alizee Zimmermann, Mya Breitbart, 19 April 2023, Science Advances.
DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adg3200
The research was funded by the National Science Foundation, Atkinson Center for Sustainable Futures Rapid Response Award, AGGRA, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, National Fish and Wildlife Foundation, Florida Keys Marine Sanctuary and the Florida Fish and Wildlife Conservation Commission.





