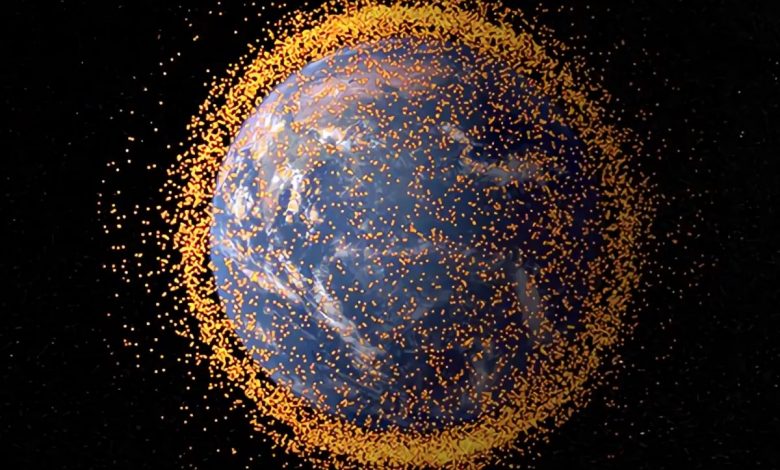
Lead image: An artist’s concept depicting the near-Earth orbital debris field, based on real data from the NASA Orbital Debris Program Office. (Image credit: NASA Goddard Space Flight Center)
In March, the U.S. Space Force’s 18th Space Control Squadron (18SPCS) reported the breakup of Yunhai 1-02, a Chinese military satellite that launched in September 2019. It was unclear at the time whether the spacecraft had suffered some sort of failure — an explosion in its propulsion system, perhaps — or if it had collided with something in orbit.
We now know that the latter explanation is correct, thanks to some sleuthing by astrophysicist and satellite tracker Jonathan McDowell, who’s based at the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics in Cambridge, Massachusetts. “This looks to be the first major confirmed orbital collision in a decade,” Jonathan McDowell, who spotted the probable crash in a data log from the US Space Force, said on Twitter.
On Saturday (Aug. 14), McDowell spotted an update in the Space-Track.org catalog, which the 18SPCS makes available to registered users. The update included “a note for object 48078, 1996-051Q: ‘Collided with satellite.’ This is a new kind of comment entry — haven’t seen such a comment for any other satellites before,” McDowell tweeted on Saturday.
He dove into the tracking data to learn more. McDowell found that Object 48078 is a small piece of space junk — likely a piece of debris between 4 inches and 20 inches wide (10 to 50 centimeters) — from the Zenit-2 rocket that launched Russia’s Tselina-2 spy satellite in September 1996. Eight pieces of debris originating from that rocket have been tracked over the years, he said, but Object 48078 has just a single set of orbital data, which was collected in March of this year.
“I conclude that they probably only spotted it in the data after it collided with something, and that’s why there’s only one set of orbital data. So the collision probably happened shortly after the epoch of the orbit. What did it hit?” McDowell wrote in another Saturday tweet.
Yunhai 1-02, which broke up on March 18, was “the obvious candidate,” he added — and the data showed that it was indeed the victim. Yunhai 1-02 and Object 48078 passed within 0.6 miles (1 kilometer) of each other — within the margin of error of the tracking system — at 3:41 a.m. EDT (0741 GMT) on March 18, “exactly when 18SPCS reports Yunhai broke up,” McDowell wrote in another tweet.
Thirty-seven debris objects spawned by the smashup have been detected to date, and there are likely others that remain untracked, he added.
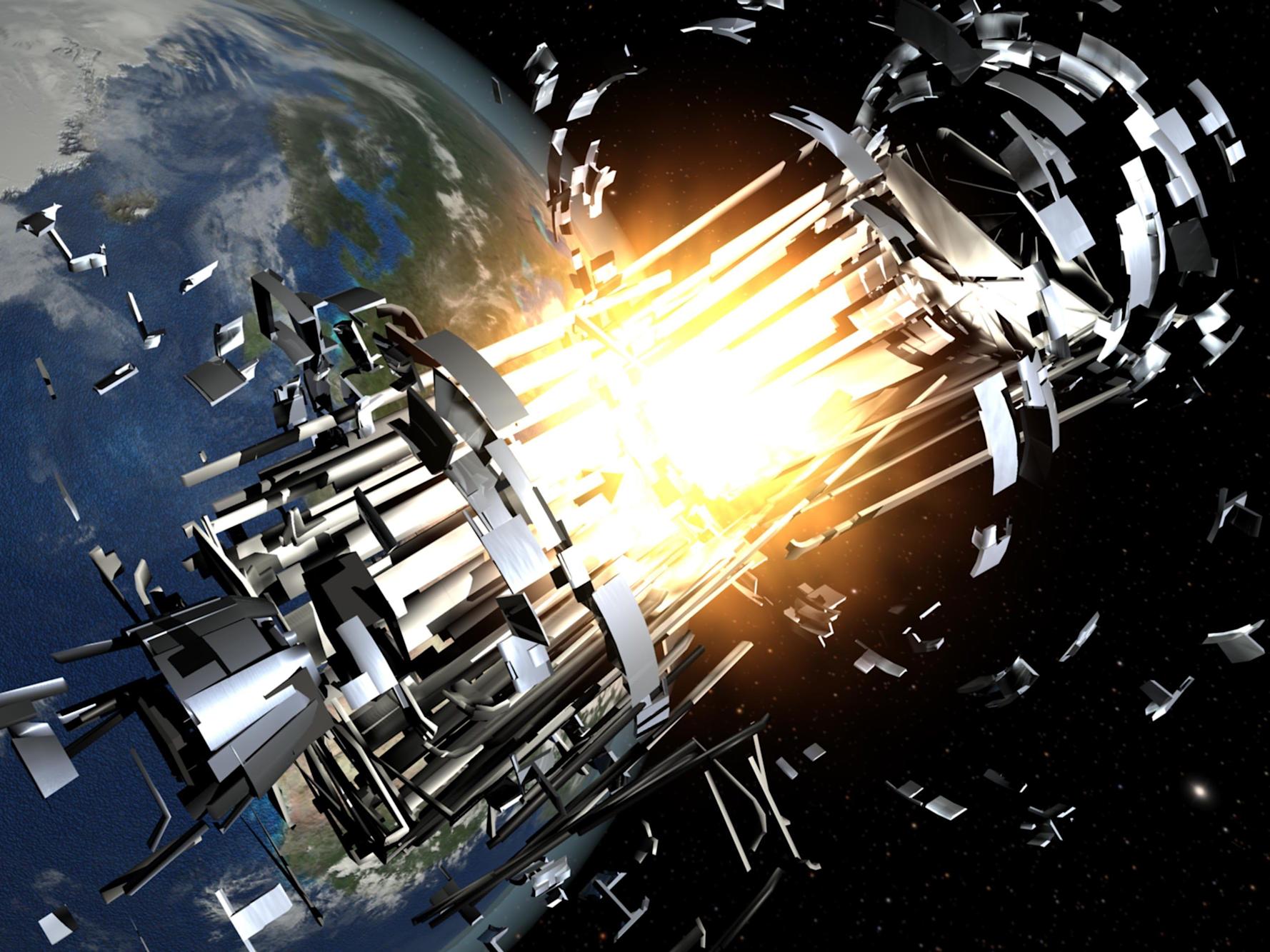

Despite the damage, Yunhai 1-02 apparently survived the violent encounter, which occurred at an altitude of 485 miles (780 kilometers). Amateur radio trackers have continued to detect signals from the satellite, McDowell said, though it’s unclear if Yunhai 1-02 can still do the job it was built to perform (whatever that may be).
McDowell described the incident as the first major confirmed orbital collision since February 2009, when the defunct Russian military spacecraft Kosmos-2251 slammed into Iridium 33, an operational communications satellite. That smashup generated a whopping 1,800 pieces of trackable debris by the following October.
However, we may be entering an era of increasingly frequent space collisions — especially smashups like the Yunhai incident, in which a relatively small piece of debris wounds but doesn’t kill a satellite. Humanity keeps launching more and more spacecraft, after all, at an ever-increasing pace.
“Collisions are proportional to the square of the number of things in orbit,” McDowell told Space.com. “That is to say, if you have 10 times as many satellites, you’re going to get 100 times as many collisions. So, as the traffic density goes up, collisions are going to go from being a minor constituent of the space junk problem to being the major constituent. That’s just math.”
We may reach that point in just a few years, he added.
The nightmare scenario that satellite operators and exploration advocates want to avoid is the Kessler syndrome — a cascading series of collisions that could clutter Earth orbit with so much debris that our use of, and travel through, the final frontier is significantly hampered.
Our current space junk problem is not that severe, but the Yunhai event could be a warning sign of sorts. It’s possible, McDowell said, that Object 48078 was knocked off the Zenit-2 rocket by a collision, so the March smashup may be part of a cascade.
“That’s all very worrying and is an additional reason why you want to remove these big objects from orbit,” McDowell told Space.com. “They can generate this other debris that’s smaller.”
Already, nearly 130 million bits of space junk surround Earth – from abandoned satellites, spacecraft that broke apart, and other missions. That debris travels at roughly 10 times the speed of a bullet, which is fast enough to inflict disastrous damage to vital equipment, no matter how small the pieces. Such a hit could kill astronauts on a spacecraft.
Small debris is tough to track, and there’s already a lot of it up there. About 900,000 objects between 0.4 inches and 4 inches wide (1 to 10 cm) are whizzing around our planet, the European Space Agency estimates. And Earth orbit hosts 128 million pieces of junk 0.04 inches to 0.4 inches (1 mm to 1 cm) in diameter, according to ESA.
Orbiting objects move so fast — about 17,150 mph (27,600 kph) at the altitude of the International Space Station, for example — that even tiny shards of debris can do serious damage to a satellite.