Latest Articles
-
Jun- 2023 -6 JuneClimate Change

When Going Green Goes Wrong: The Human Rights Paradox of Decarbonization
Lead Image: The drive towards decarbonization and renewable energy presents a significant challenge regarding social justice, especially impacting indigenous peoples and disadvantaged communities. The concept of a ‘just transition’ insists that the cost of the energy overhaul shouldn’t disproportionately impact the vulnerable. However, infrastructural inequalities and costs hinder the accessibility of renewable energy for disadvantaged communities, reinforcing energy insecurity. Columbia Climate School researchers are exploring these social, ethical, and environmental conflicts, recommending more targeted assistance programs to ensure a fair transition. Mining, Land Grabs, and More: When Decarbonization Conflicts With Human Rights The shift to renewable energy is exacerbating social…
Read More » -
4 JuneUncategorized
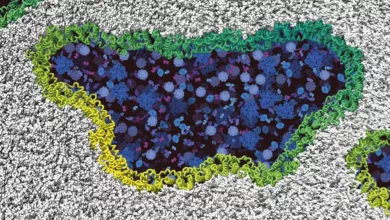
How Our Cells Kill Themselves – Scientists Decode the Exact Mechanism at the Atomic Level
Ninjurin-1 proteins assemble (green/yellow) into filaments and rupture the cell membrane (gray) until the cell disintegrates completely. Intracellular components are shown in blue. Credit: Biozentrum, University of Basel In our bodies, millions of cells meet their end on a daily basis. Contrary to popular belief, cells don’t just explode when they die. Instead, a particular protein acts as a trigger for the rupture of the cell membrane. Scientists from the University of Basel have recently been able to elucidate the exact mechanism at the atomic level. Their findings are published in the journal Nature. The self-elimination of cells is a…
Read More » -
2 JuneDNA

The Dawn of Diversity: Release of the New Human Pangenome Reference
The Human Pangenome Reference Consortium has introduced a significantly more diverse reference human genome sequence, the “pangenome,” composed of 94 distinct genome sequences and aiming to reach 700 by 2024, which helps in identifying larger genomic variants and enhancing genomic analysis accuracy. More complete and sophisticated collection of genome sequences captures significantly more human diversity. Researchers have released a new high-quality collection of reference human genome sequences that captures substantially more diversity from different human populations than what was previously available. The work was led by the international Human Pangenome Reference Consortium, a group funded by the National Human Genome…
Read More » -
May- 2023 -31 May3D Printing

3D Printing Paves Way for “Designer” Titanium Alloys
A collaborative research team has developed a new class of titanium alloys that are strong and ductile rather than brittle. The innovative design combines the use of alloy with 3D-printing processes, potentially revolutionizing applications in sectors like aerospace, biomedical, chemical engineering, space, and energy. These alloys comprise a blend of alpha-titanium and beta-titanium phases, with the added use of oxygen and iron as stabilizers and strengtheners. Researchers have developed a new class of ductile and strong titanium alloys using a combination of alloy design and 3D printing. The findings, published in Nature, could revolutionize applications in various sectors, including aerospace…
Read More » -
30 MayAI

AI Battles Superbugs: Helps Find New Antibiotic Drug To Combat Drug-Resistant Infections
Lead Image: AI technology has helped MIT and McMaster University researchers identify a new antibiotic named abaucin, effective against Acinetobacter baumannii, a hospital-borne, drug-resistant bacteria. The drug, discovered through a machine-learning model, is significant due to its narrow-spectrum efficacy and unique mechanism of disrupting lipoprotein trafficking within bacterial cells. The machine-learning algorithm identified a compound that kills Acinetobacter baumannii, a bacterium that lurks in many hospital settings. Using an artificial intelligence algorithm, researchers at MIT and McMaster University have identified a new antibiotic that can kill a type of bacteria that is responsible for many drug-resistant infections. If developed for…
Read More »